WOMEN’S CANCER
Cancer is the major cause of deaths in Malaysia. The word “Cancer” generates fear not only among the victims but also the public. The objective of this pamphlet is to educate women on cancer as well as to remove fears and misconception about cancer.
WHAT IS CANCER?
Cancer is a large group of diseases characterised by uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. Normal cells reproduce in an orderly manner and grow for a purpose as in a growing child, or to replace worn-out tissue or repair injuries. Cancer cells on the other hand grow for no reason. They multiply uncontrollably, destroy normal cells, and can spread to other parts of the body.
CAUSES OF CANCER
The exact mechanism that causes cancer is still unclear. But several factors have been identified as carcinogenic or cancer-producing. These include smoking, exposure to subtances like fluoracarbons and asbestos, certain chemicals, radiation, and excessive exposure to sunlight. A small proportion of cancers may be hereditary. Viruses may also play a role in some cancers such as leukemia, nasopharyngeal cancer, liver and cervical cancers.
CAN CANCER BE PREVENTED?
Some cancers can be prevented but not all. For example, most lung cancers can be prevented by not smoking and most skin cancers can be prevented by avoiding excessive sun and using protective sun screens.
Although many cancers cannot be prevented death can be prevented by early detection & proper treatment. Let us look at cancer in women and what you can do to protect yourself. While cancer can occur in any part of the body the following are some common sites – Breast, Colorectum, Cervix, Lung, Stomach, Ovary, Skin, Naso-pharynx, Liver and Thyroid.
In this article, we shall discuss two of the commonest cancers in women, namely of the Breast and Cervix.
BREAST CANCER
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women. It occurs most often as a painless lump or thickening, in the upper outer part of the breast. More than 90% of breast cancer are discovered by the women herself. If detected early, it is curable.
There may be a higher chance of breast cancer among women who:
- (a) Are over 35 years old
- (b) Have early menstruation or late menopause
- (c) Have a family history of breast cancer
- (d) Have their first child after 30 years of age or are childless
Signs
- (a) A lump or swelling (usually painless) in the breast or armpit
- (b) Blood or unusual discharge from the nipple
- (c) Nipple becomes pulled in
- (d) The skin over the breast becomes puckered or dimpled
- (e) Rash around the nipple (rare)
- (f) Pain is rarely an early symtom of breast cancer
Note: Nine out of ten lumps in the breast (especially in younger women are harmless). Often they are cysts (collection of fluid) and may or may not be painful.
Detection Of Breast Cancer
- Breast Self-Examination (BSE): Most lumps are detected during self-examination of the breast. Every woman should exmine her breast once every month.
- Mammography: X-ray examination of the breast to detect lumps, is recommended as follows:
– a base-line breast x-ray at age 40
– breast x-ray every 1-2 years till 50 years and then yearly after that. - Regular breast examination by a doctor
HERE IS HOW YOU DO BSE
- In the shower: check for any lump or thickening.
- Before a mirror: Look for any changes in contour of your breasts, a swelling or dimple in the skin.
- Lying down: Put pillow under right shoulder. With fingers flat, examine right breast, press gently in small circular motions; then squeeze nipple to check for discharge. Now do left breast.
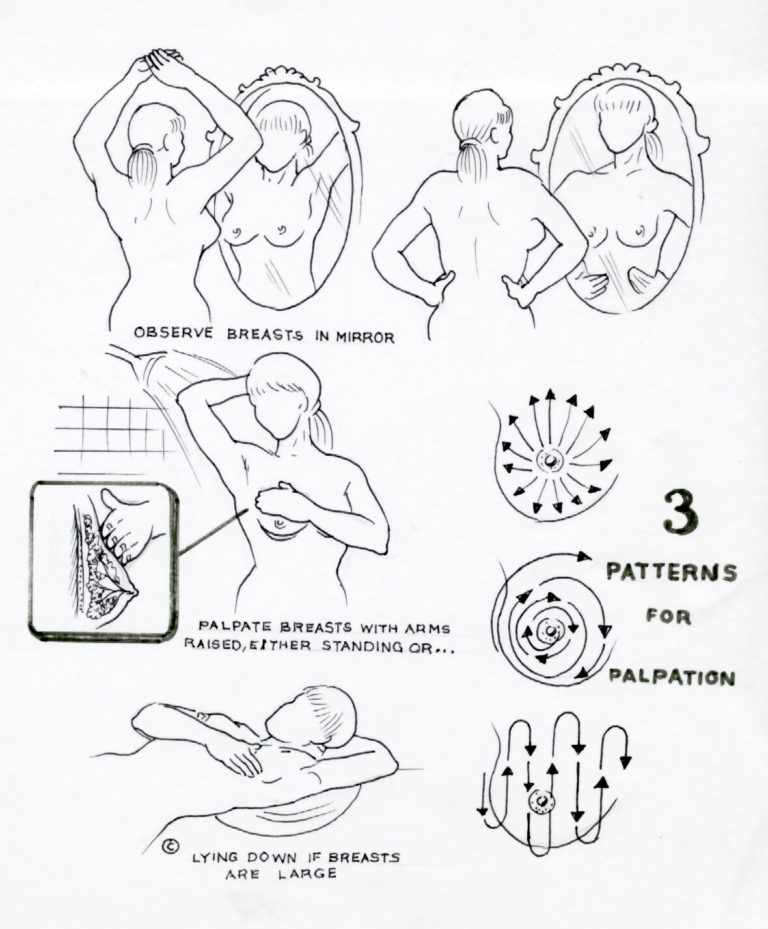
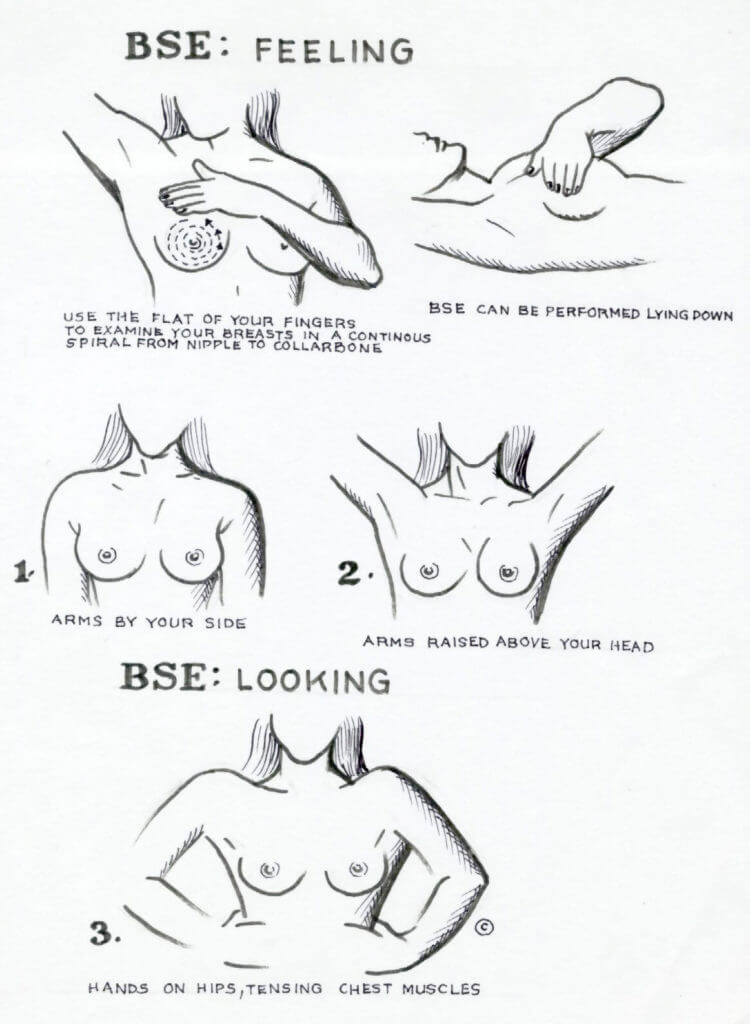
Remember
- BSE should be done monthly, just after your periods ends (or on a fixed day each month it your periods have stopped after menopause).
- With little practice you will be able to detect any abnormal lumps yourself.
- Most breast lumps however are not cancerous.
- All the same, to be sure, see a doctor soon if you feel a lump or any changes in your breast.
CERVICAL CANCER
Cervical cancer or cancer of the cervix develops in the neck of the womb. The cancer is slow growing and remains confined to the cervix for a long time. But when it does grow out of the cervix it can spread to the vagina, nearby lymph nodes and to the rectum or the bladder. No woman need die from cervical cancer as the disease is curable when discovered early.
Signs
- (a) Irregular vaginal bleeding
- (b) Vaginal Discharge
PAP SMEAR
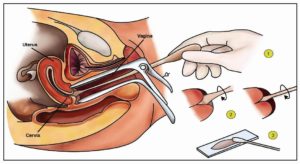 All women over the age of 18 years who are married or who have had sexual intercourse should have a PAP SMEAR test regularly. A pap smear is a collection of vaginal fluid and cells from the surface of the cervix. These cells are shed, just like normal skin cells into the vaginal fluid, and examined under the microscope to see if they are abnormal cells.
All women over the age of 18 years who are married or who have had sexual intercourse should have a PAP SMEAR test regularly. A pap smear is a collection of vaginal fluid and cells from the surface of the cervix. These cells are shed, just like normal skin cells into the vaginal fluid, and examined under the microscope to see if they are abnormal cells.
The pap smear can be done by a doctor or a trained nurse. It should be done at least every two years after 2 initial negative tests 1 year apart. The pap smear test helps to detect cancer of the cervix at a very early stage when simple treatment can result in total cure.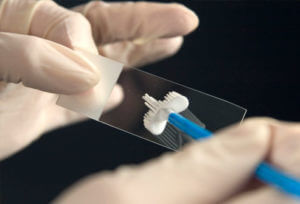
DETECTION OF OTHER CANCERS
Only some cancers are noticeable at an early stage, such as cancers on the surface of the body e.g. cancer of the skin, mouth and external genitalia. Cancers deep in the body are not noticeable and require special examination.
Routine cancer-related check-up (e.g. BSE, Pap smear test, rectal examination) are the best means of finding certain cancers early. Awareness of cancer’s eight warning signals and prompt medical attention also gives an excellent chance of successful treatment.
TREATMENT OF CANCER
Cancer can be treated by operation, radiation, anti-cancer drugs, or hormones. Hope cf cure depends on the type of cancers and the stage the cancer has reached when treatment is sought Chances of cure are good if cancer is detected early and treated properly. But even after treatment there is a possibility that the cancer may recur in some cases. Chances of recurrence depend on the type and site of the cancer and how quickly it had originally been detected and treated.
EIGHT WARNING SIGNALS OF CANCER
- A sore which refuses to heal.
- A lump or thickening in the breast or elsewhere.
- Any unusual bleeding or discharge.
- Any change in normal bowel habits.
- Any change in a mole or wart.
- Persistent indigestion or difficulty in swallowing.
- Presistent hoarseness or cough.
- Impairment of hearing with noise in the same ear.
These signals do not always mean cancer but if they persist, see your doctor at once.
If you have any of the symptoms mentioned above, please do not hesitate to contact Dr. Gan for an appointment.



Add a Comment